If your factory processes flour, wood, sugar, or metal, you should be aware of the dust explosion hazard associated with the processing or storage of these materials, which can have fatal consequences for both your facilities and personnel.
To help you understand the scale of the danger, we’ll explain what a dust explosion is, the industries at risk, and the mitigation steps you can take to prevent one from happening in the future.
What is a Dust Explosion and Why Is It More Dangerous than a Regular Fire?
A dust explosion is an event that occurs when a cloud of dust produced from solid material particles reacts chemically, is ignited by an electrical spark, or comes into contact with a hot surface.
These incidents don’t just happen. Accumulated dust must reach a certain concentration to ignite. Therefore, you need to pay extra attention to vulnerable areas such as material processing areas that use equipment like mixers, sieves, and pipes.
In reality, dust explosions often occur due to chemical reactions that cause self-combustion and ignite combustible dust clouds, even at normal temperatures. This invisible process is one of the reasons why this event is so dangerous.
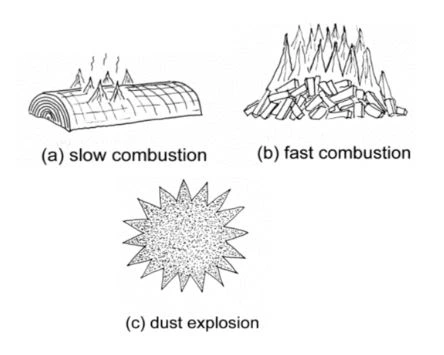
To visualize the explosive force, consider the illustration of the combustion stages of different types of wood. If you burn logs, the combustion process will be relatively slow, while the combustion of smaller pieces of wood will accelerate.
When you burn wood chips that contain smaller particles, the combustion process will accelerate more, creating a dense cloud that easily ignites. This is because the wood has a larger surface area in contact with the air.
This illustrates the nature of dust explosions, which easily spread, resulting in severe damage. Furthermore, dust explosions also carry the risk of secondary explosions, potentially causing total destruction to your factory.
Industries at Risk: Is Your Factory Included?
Not all factories are at risk of dust explosions, but rather those that process or produce materials that readily react with oxygen. Here’s a list.
Food Industry (Flour, Sugar, Coffee)
Factories that convert solid organic materials into powders, such as flour, sugar, wheat, and rice, are at high risk of dust explosions. Furthermore, factories that grind coffee, chocolate, animal feed, spices, and starch are also susceptible to these incidents.
Wood & Furniture Manufacturing Industry

Another organic material outside the food industry that is at high risk of dust explosions is wood. This includes factories that process logs, pulp and paper, and businesses engaged in furniture.
Metal & Pharmaceutical Industry
Dust explosion hazards can also occur in factories that process metal powders, potentially forming fine dust suspended in the air, such as zinc, aluminum, iron, and similar materials. Beyond metals and food, factories that process pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and other industries that process synthetic organic materials are also at risk.
Mitigation Solutions According to NFPA 652 Standard
To avoid dust explosions, you can take several precautions, such as adding inert gas to reduce the oxygen content in the room. You also need to implement work systems that minimize the risk of sparks.
Furthermore, it is important to control material storage methods to prevent self-combustion or to incorporate fire hydraulic calculations into your factory’s fire protection system design.
Besides that, you also need to implement the NFPA 652 safety standard by installing several relevant systems. Here’s a more complete explanation.
Spark Detection System
The first step is to install a spark detector, which works by detecting infrared light that indicates ember particles. If the detector is triggered, the water spray nozzle will activate to extinguish the spark before it can cause an explosion.
Explosion Venting System
In addition to initial extinguishing, the system also needs to be supported by an explosion ventilation system, which functions to divert fire pressure to a safer area. This system is essential if a fire ignites and cannot be extinguished in its initial stages. Furthermore, this ventilation also helps prevent structural damage to your factory.
Why Do You Need a Fire Engineer Consultant to Analyze Your Dust Risk?
In addition to installing these two systems, the NFPA also requires every facility at risk of dust explosions to conduct a Dust Hazard Analysis (DHA), which is an effort to identify the scale of the hazard posed by combustible dust to determine appropriate mitigation measures.
To conduct this analysis, you cannot do it yourself; you need to consult with a fire engineer with extensive expertise in evaluating risks and designing effective prevention and mitigation systems.
Make sure you choose the right fire engineering consultant to ensure the strategic steps provided are tailored to your needs. Like Lumeshield, a consultant with a team of over 10 years of experience conducting fire risk assessments for client facilities across various industries, including DHA analysis.
We use a data-driven approach to produce accurate analyses and then recommend systems tailored to your facility’s needs. We are also skilled at creating a fire protection system design based on the assessment results.
We ensure that our methods and system designs adhere to SNI, NFPA, and FM Global, ensuring your facility’s fire protection system complies with applicable safety standards. Call us now to prevent a dust explosion that threatens lives!

