Creating an effective and easily accessible fire evacuation plan is essential to prevent loss of life in the event of a fire. However, many building managers sometimes overlook important aspects that should be a primary consideration.
In this article, we will guide you through the criteria and essential components of designing a safe fire evacuation route, and also some common mistakes you need to avoid.
What are the Criteria for a Safe Evacuation Plan?
Before planning an evacuation path, keep these criteria in mind to ensure the track meets safety standards.
Evacuation routes must be clear and well-lit
Ensure that the path to the emergency exit is safe, smooth, and clear of objects that could potentially hinder the evacuation process. Emergency exit doors must be easy to open and have sufficient corridors for all building occupants to pass through.
You can start by creating an accurate evacuation map based on the fire risk assessment of your building. Choose an area that is safe from gas installations, smoke, and fire, but still accessible to users for an efficient evacuation process.
Furthermore, exit tracks must be well-lit. Differentiate lighting sources so that if the main lighting is affected by a fire, lighting on the evacuation track is not disrupted.
Install comprehensive evacuation signage
Ensure that users can clearly see and understand signs leading to the evacuation corridor. This includes emergency exit signs, directions to the assembly point, and signs for the assembly point itself. You must also adhere to the color requirements for signs, which are green and white for borders, symbols, letters, and numbers.
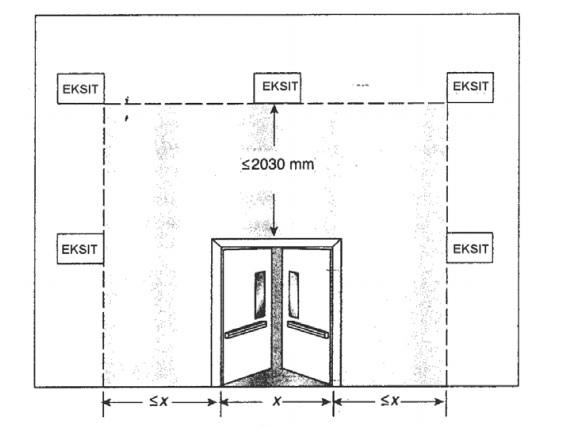
Emergency exit facilities and signs must comply with regulations
Corridors or tunnels for an emergency track must be adequately wide, at least 1.2 meters. Make sure that it is non-slip and easily passable by users.
Additionally, you must ensure that exit signs comply with K3 evacuation route regulations, including Peraturan Menteri Ketenagakerjaan, Peraturan Menteri Pekerja Umum, and SNI, which can be summarized in the following provisions:
- Must be visible and tangible
- If installed vertically, it must not be more than 20 cm above the emergency exit door
- If installed near the floor surface, the distance from the floor must be 15-20 cm
- The distance to the next sign must not exceed 30 m
Important Components of An Evacuation Plan
You also need to consider three important components in designing an evacuation map. Here is a list:
Signage
This is the primary element that helps users understand the evacuation process independently in the event of a fire. Therefore, it is important to consider the appropriate and visible placement of signs and directions.
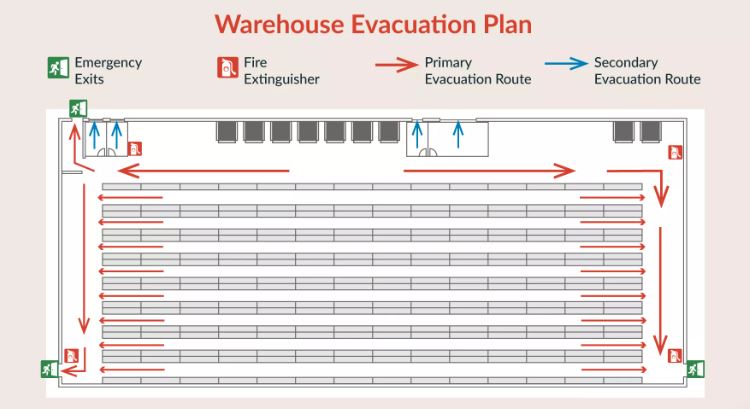
For example, here is an evacuation map for a storage warehouse created by Alert Media, a UK-based emergency communications company. This map clearly shows the locations of directional signs, such as emergency exits, fire extinguisher locations, and also primary and secondary emergency tracks.
With clear visualization, users can quickly understand which direction to go in the event of a fire. Furthermore, marking the location of aids such as fire extinguishers also facilitates faster fire response.
Emergency Lights
As previously explained, you must separate the power supply for lighting evacuation path. Lighting is crucial for guiding users out of the building safely. Inadequate lighting can potentially slow down the evacuation process.
Assembly Point
An assembly point refers to an open space free from trees, power lines, and away from tall buildings. Determining the assembly point is also important, whether you will use a parking lot, field, or other area outside the building that is considered safe during a fire.
Common Mistakes in Designing Emergency Evacuation Plan
If you feel you’ve implemented the steps we’ve recommended above, but the evacuation isn’t going according to plan, you may be neglecting the following:
1. The path isn’t clear of obstacles, sometimes there’s still a buildup of luggage in the corridors, or the exit doors are damaged or jammed.
2. Unclear emergency signage can confuse users. Remember, signage plays a crucial role in guiding them during the evacuation process.
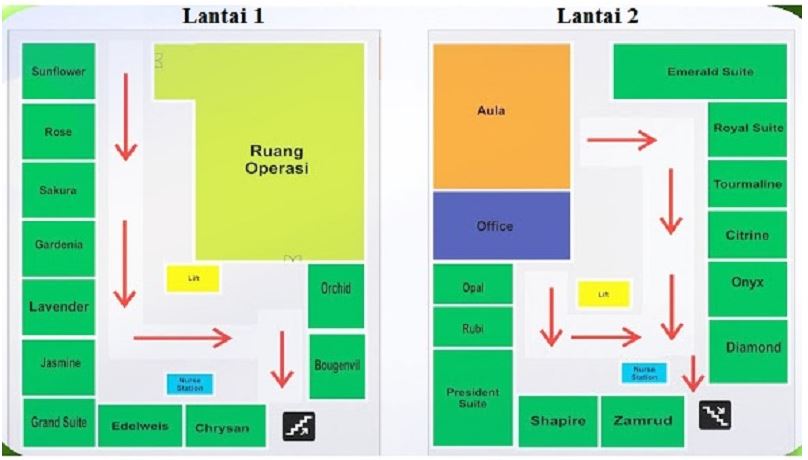
Here is an example of an evacuation map that doesn’t adequately guide users. The map doesn’t clearly indicate the location of emergency exits. The arrows are also not clearly defined.
3. Lack of adequate lighting, poorly maintained lighting, or if electrical lines are not separated from the main power supply, they can disrupt lighting in the emergency path when a short circuit occurs.
4. Unsafe assembly points, sometimes it is too close to buildings, trees, or power lines that could fall at any time.
5. The lack of regular inspections of evacuation tracks can lead to space conversions, such as the accumulation of goods, or the lack of maintenance of lighting systems.
6. Creating an evacuation map for the sake of compliance is a fatal mistake because the primary design mindset fails to prioritize human life.
7. Lack of evacuation training is also a factor in hindering evacuation processes, as not all building users have the quick and reliable response to escape. Therefore, the following discussion regarding evacuation drills is important for you to understand.
The Importance of Regular Fire Drills
In addition to accurate evacuation route planning, you also need to train building users through fire simulations. These drills are intended to increase safety awareness for each individual.
Fire drills also help develop a quick and organized response to emergencies. In essence, this training helps each user become familiar with the evacuation process so that when a fire occurs, they understand what to do. To conduct an effective fire drill, you can follow this guide.
Most importantly, this training can also help test the effectiveness of the evacuation route you’ve created. You can improve any components that become obstacles during the fire drill so that the system can function optimally when a fire actually occurs.
Conclusion
This concludes our guide to designing an effective fire evacuation route. In the future, you must consider the safe criteria and mandatory components of an evacuation plan before designing. You also need to conduct evacuation training for users so they develop good safety reflexes in the event of a fire.
As experts in the field, Lumeshield always implements fire protection system designs that comply with government regulations, SNI, and even international industry standards. We always prioritize human life in every design we create.
We can also help you plan accurate evacuation routes and implement standard maintenance procedures to keep your safety system in good condition. Contact us for a consultation on fire evacuation design planning to the highest standards.

